The Internal Combustion Engine: An In-Depth Look into the Heart of Your Car
Have you ever wondered how your car's engine works? How it transforms fuel into energy that propels your car forward? The answer is the internal combustion engine, a marvel of engineering that has powered cars for over a century.
In this article, we'll take a closer look at the internal combustion engine, from its history to its components, and how it operates. So buckle up and get ready for a fascinating ride through the heart of your car!
A Brief History of the Internal Combustion Engine
The internal combustion engine has a long and storied history, dating back to the late 1800s. In 1876, a German engineer named Nikolaus Otto invented the four-stroke engine, which became the basis for the modern internal combustion engine.
Over the years, the internal combustion engine has undergone countless improvements and refinements, with the goal of making it more efficient, powerful, and environmentally friendly.
Today, most cars use a type of internal combustion engine called a spark-ignition engine, which runs on gasoline or a mixture of gasoline and ethanol. Diesel engines, which are used in some cars and trucks, run on diesel fuel.
How Does an Internal Combustion Engine Work?
The internal combustion engine is a complex piece of machinery that converts fuel into mechanical energy. It does this by burning fuel inside a cylinder, which produces a high-pressure gas that pushes a piston.
The process begins with the intake stroke, where the piston moves down the cylinder, creating a vacuum that draws in a mixture of fuel and is then compressed by the piston during the compression stroke, which increases the pressure and temperature inside the cylinder.
Next comes the power stroke, where a spark from the spark plug ignites the fuel-air mixture, causing it to burn rapidly and release energy. This energy pushes the piston back down the cylinder, creating mechanical force that can be used to turn the car's wheels.
Finally, during the exhaust stroke, the piston moves back up the cylinder, pushing the burned gases out of the engine and into the car's exhaust system.
This process repeats itself many times per second, producing the continuous rotation of the engine's crankshaft that powers the car.
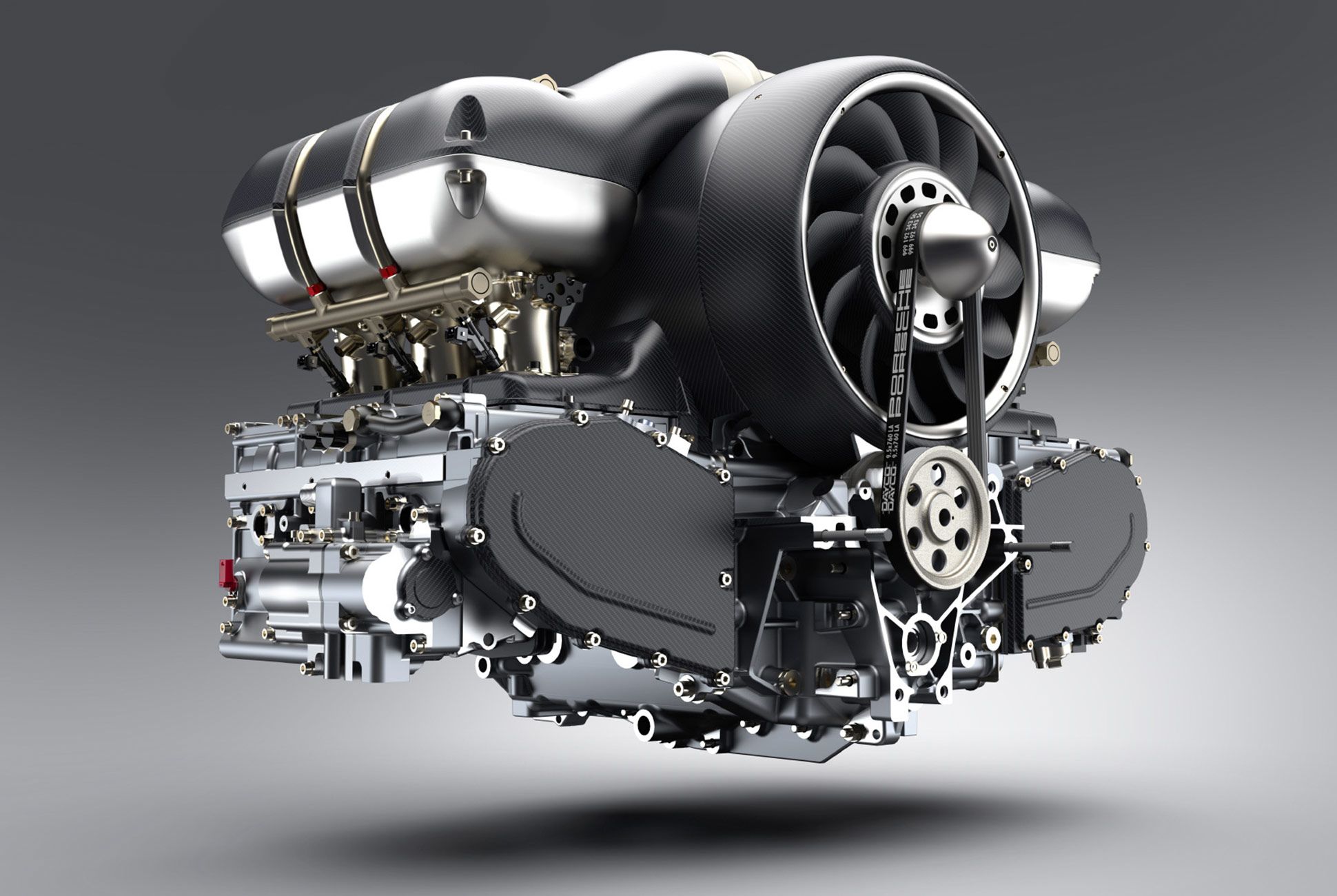
Internal Combustion Engine Components
Now that we've looked at how the internal combustion engine works, let's take a closer look at its components.
The engine block is the foundation of the engine and houses the cylinders, pistons, and crankshaft. The cylinder head sits on top of the engine block and contains the valves and spark plugs.
The pistons move up and down inside the cylinders, powered by the force of the expanding gas. The crankshaft converts the up-and-down motion of the pistons into the rotary motion needed to turn the car's wheels.
The valves control the flow of fuel and air into the cylinders and the exhaust gases out of the engine. The spark plugs ignite the fuel-air mixture, starting the combustion process.
Other important components of the internal combustion engine include the fuel injectors, which spray fuel into the cylinders at precise intervals, and the timing belt or chain, which synchronizes the movement of the pistons and valves.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Internal Combustion Engines
While internal combustion engines have powered cars for over a century, they are not without their drawbacks.
One of the main drawbacks of internal combustion engines is their environmental impact. They produce harmful emissions like carbon dioxide, which contributes to climate change, and nitrogen oxides, which can lead to smog and respiratory problems.
In recent years, there has been a push towards more environmentally friendly engines, such as hybrid and electric engines. However, internal combustion engines still have some benefits over these newer technologies.
One of the main benefits of internal combustion engines is their power output. They are capable of producing large amounts of torque and horsepower, making them ideal for high-performance cars and heavy-duty vehicles like trucks and SUVs.
Additionally, internal combustion engines are widely available and relatively cheap to produce, which makes them accessible to a wide range of consumers.
Labels: automobile, Interesting, Technology

0 Comments:
Post a Comment
Subscribe to Post Comments [Atom]
<< Home